Plant fibers are sourced and processed through various methods to make a wide range of end products. The process can vary depending on the type of plant fiber being used and the desired end product. Here's a general overview of how plant fibers are sourced and processed:
Sourcing Plant Fibers:
Cultivation: Many plant fibers come from specific plants cultivated for their fiber content. Examples include cotton (from the cotton plant), jute (from the jute plant), and hemp (from the hemp plant).
Harvesting: Once the plants reach maturity, they are harvested to obtain the fibers. Some fibers, like cotton, are harvested from the seeds (cotton bolls), while others come from the stem or outer layers of the plant.
Retting (Natural Process):
Some plant fibers, such as flax and jute, undergo a natural process called retting. This involves soaking the harvested plants in water or exposing them to moisture to allow the fibers to separate from the woody parts of the plant.
After retting, the fibers are extracted manually or mechanically from the softened plant material.
Decortication (Mechanical Process):
For certain fibers, like sisal and hemp, decortication is used to remove the fibers from the plant. This mechanical process involves crushing and scraping the plant material to separate the fibers.
Fiber Extraction:
Once the fibers are separated from the plant material, they are cleaned and further processed to remove impurities, such as dirt, leaves, and other non-fiber elements.
Fiber Treatment:
Depending on the end product, the fibers may undergo additional treatments. For example, cotton fibers may be bleached and dyed to achieve desired colors, while linen fibers (from flax) may be scoured to remove waxes and lignin.
Spinning:
Spinning is a critical step in turning plant fibers into yarns. The fibers are twisted together to form continuous strands that can be woven or knitted into fabrics.
Weaving, Knitting, or Nonwoven Production:
The yarns are used to create various end products through weaving (interlacing yarns on a loom), knitting (looping yarns together), or nonwoven processes (bonding fibers together without weaving or knitting).
Finishing:
After the end product is created, it undergoes finishing processes such as dyeing, printing, and applying any necessary coatings or treatments to enhance its appearance, functionality, and durability.
The specific processing steps and techniques can vary significantly depending on the type of plant fiber and the intended use of the end product. Different cultures and regions have their traditional methods of processing plant fibers, resulting in a diverse array of textiles and materials with unique properties and characteristics.
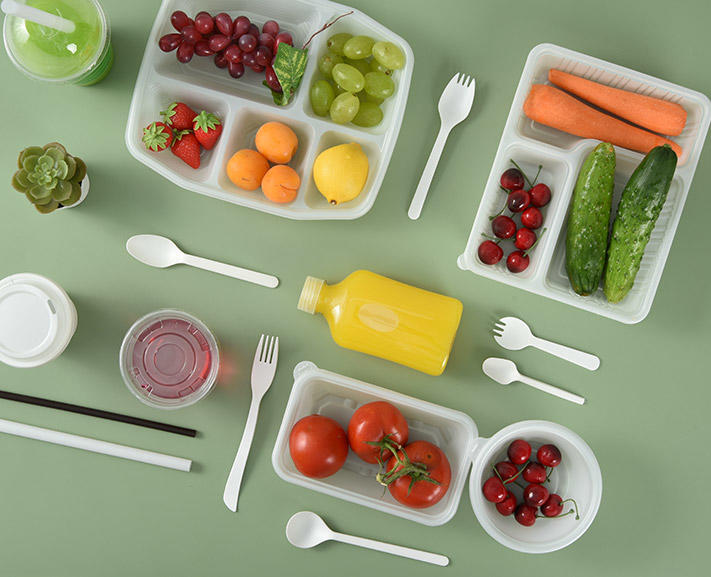
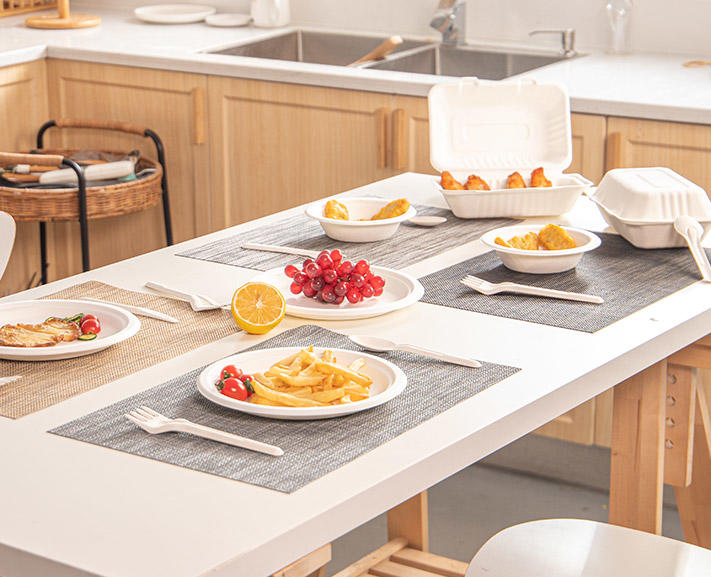
- Disposable Biodegradable Tableware
- Disposable Biodegradable Straws
- Biodegradable Film&bag
- Biodegradable Tableware
- Disposable Biodegradable cup
- Plant Fibres Packing Box
- Plant Fibres Dinner Plate
- Plant Fibres Knife and Fork
- Plant Fibres Cup
- Plant fiber paper straws
Explore what we’re saying, what we’re sharing and what we’re thinking.
Read More









 English
English 日本語
日本語 Deutsch
Deutsch

