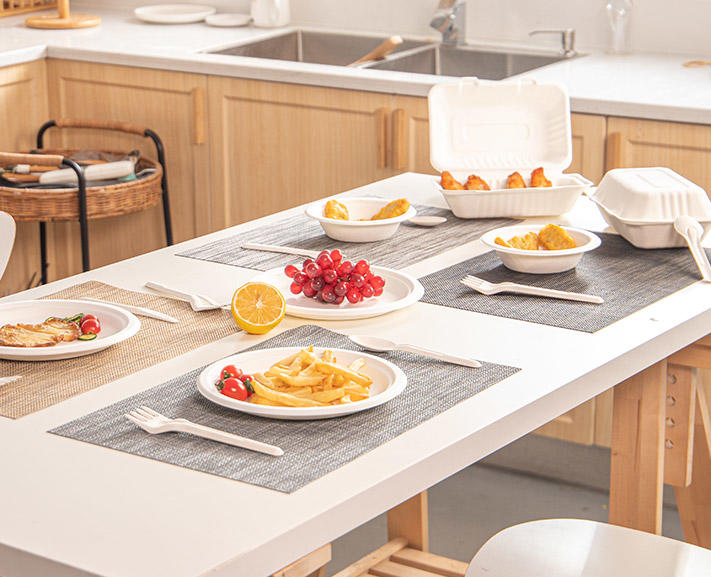
The global shift toward eco-friendly alternatives has propelled biodegradable disposable plates into the spotlight. Unlike traditional plastic or Styrofoam tableware, these plates decompose naturally, minimizing environmental harm. But how exactly are they produced?
1. Raw Material Selection: The Foundation of Sustainability
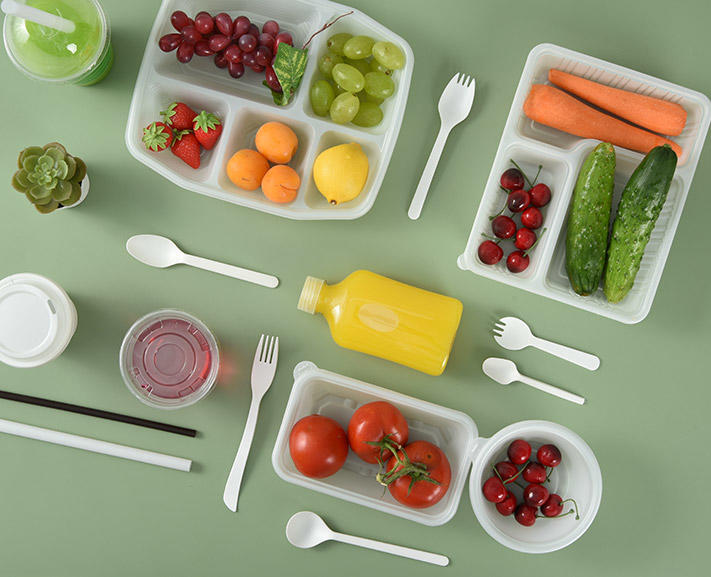
Biodegradable plates are crafted from renewable, plant-based materials. Common sources include:
Sugarcane Bagasse: A fibrous byproduct of sugarcane processing, rich in cellulose.
Bamboo Fiber: Fast-growing bamboo pulp, known for its strength and antibacterial properties.
Palm Leaves: Fallen palm leaves collected without harming trees.
Cornstarch (PLA): Polylactic acid derived from fermented corn sugars, forming a compostable polymer.
These materials are chosen for their low environmental footprint, rapid renewability, and compatibility with industrial composting systems.
2. The Manufacturing Process: From Waste to Functional Tableware
Step 1: Raw Material Preparation
Natural fibers undergo rigorous cleaning to remove impurities. For example, sugarcane bagasse is washed to eliminate residual sugars and dried to reduce moisture. Bamboo or palm leaves are sterilized and mechanically shredded into fine pulp.
Step 2: Pulp Mixing and Binding
The processed fibers are blended with water and natural binders (e.g., plant starches or food-grade glycerin) to form a malleable pulp. For PLA-based plates, cornstarch is heated and molded into resin pellets.
Step 3: Hydraulic Pressing and Molding
The pulp is fed into high-pressure hydraulic molds. Heat (150–200°C) and pressure (up to 300 tons) compress the fibers into plate shapes. This step eliminates the need for synthetic adhesives, ensuring 100% biodegradability. PLA pellets are melted and injection-molded into durable, heat-resistant plates.
Step 4: Drying and Finishing
Newly formed plates are oven-dried to solidify their structure. Edges are trimmed, and surfaces may be embossed for aesthetics or coated with natural waxes for water resistance.
3. Quality Assurance: Meeting Industry Standards
Biodegradable plates must comply with international certifications like ASTM D6400 (compostability) or EN 13432 (EU biodegradability standards). Key tests include:
Decomposition Testing: Plates are buried in industrial compost to verify breakdown within 90–180 days.
Tensile Strength Analysis: Ensures plates withstand typical food weights (e.g., 500g–1kg).
Chemical Safety Checks: Confirming no toxic residues from dyes or binders.
4. Environmental Advantages Over Conventional Plastics
Carbon Footprint Reduction: Plant-based materials absorb CO₂ during growth, offsetting emissions.
Waste Diversion: Biodegradable plates decompose into water, CO₂, and biomass, avoiding microplastic pollution.
Energy Efficiency: Production consumes 65% less energy than plastic manufacturing.
5. The Future of Biodegradable Tableware
The market for biodegradable plates is projected to grow at a CAGR of 6.2% through 2030, driven by corporate sustainability goals and consumer demand. Innovations like algae-based bioplastics and 3D-printed edible cutlery hint at a zero-waste future.
Disposable biodegradable plates exemplify how industrial processes can align with ecological stewardship. By transforming agricultural waste into functional products, manufacturers reduce landfill burden while offering consumers a guilt-free alternative. For businesses, embracing biodegradable tableware isn’t just ethical—it’s a strategic response to a planet-conscious market.










 English
English 日本語
日本語 Deutsch
Deutsch

